Connecting Users and Devices to iboss cloud – Traffic Redirection Methods
The iboss cloud provides many options for connecting users and devices to cloud security. This solution brief discusses various options and choices available to easily secure Internet access in the cloud for users and devices across an organization.
Connecting Users and Networks to iboss Overview
The iboss cloud platform provides a large array of choices for connecting users to cloud security. The options provide the flexibility needed to support diverse networks and organizations. This solution brief does not include all of the methods available for connecting users to the iboss cloud platform. Rather, it provides common methods that are typically used to connect users and networks to iboss cloud.
At a high level, there are two general use cases that drive decisions of how to connect to the iboss cloud:
- Mobile users which are using organizationally owned devices but are accessing the Internet on networks the organization does NOT control. Coffee shops and airports are good examples of this.
- Users that are accessing the Internet within networks controlled by the organization. Headquarters or remote offices are examples of this.
The two scenarios above are important because they introduce network limitations outside of an administrator’s control. For example, as a network administrator you cannot call the local coffee shop and ask them to reconfigure their networking equipment because employees might be buying coffee there and using that Wi-Fi network occasionally.
Cloud Connectivity and User Authentication
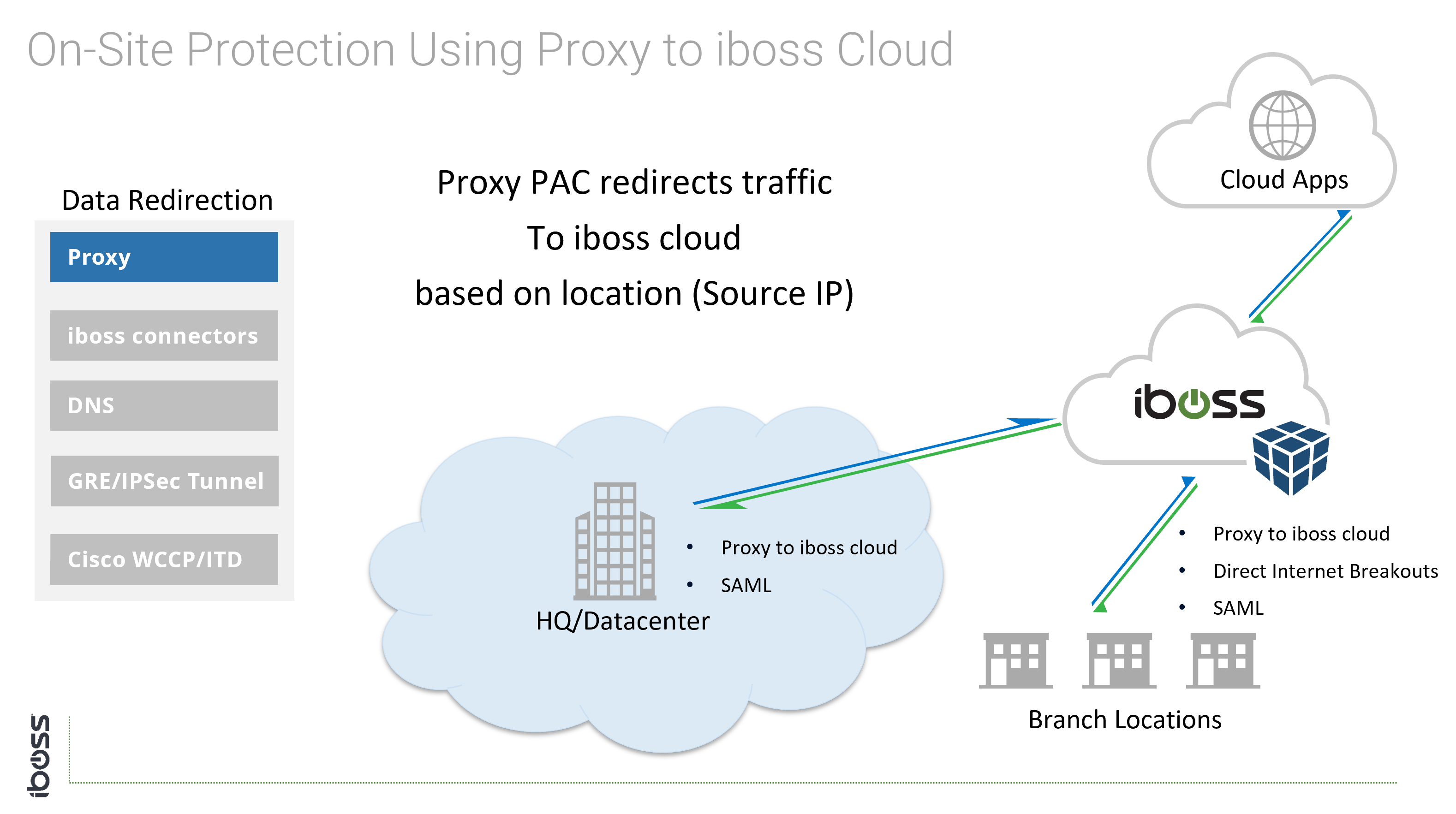
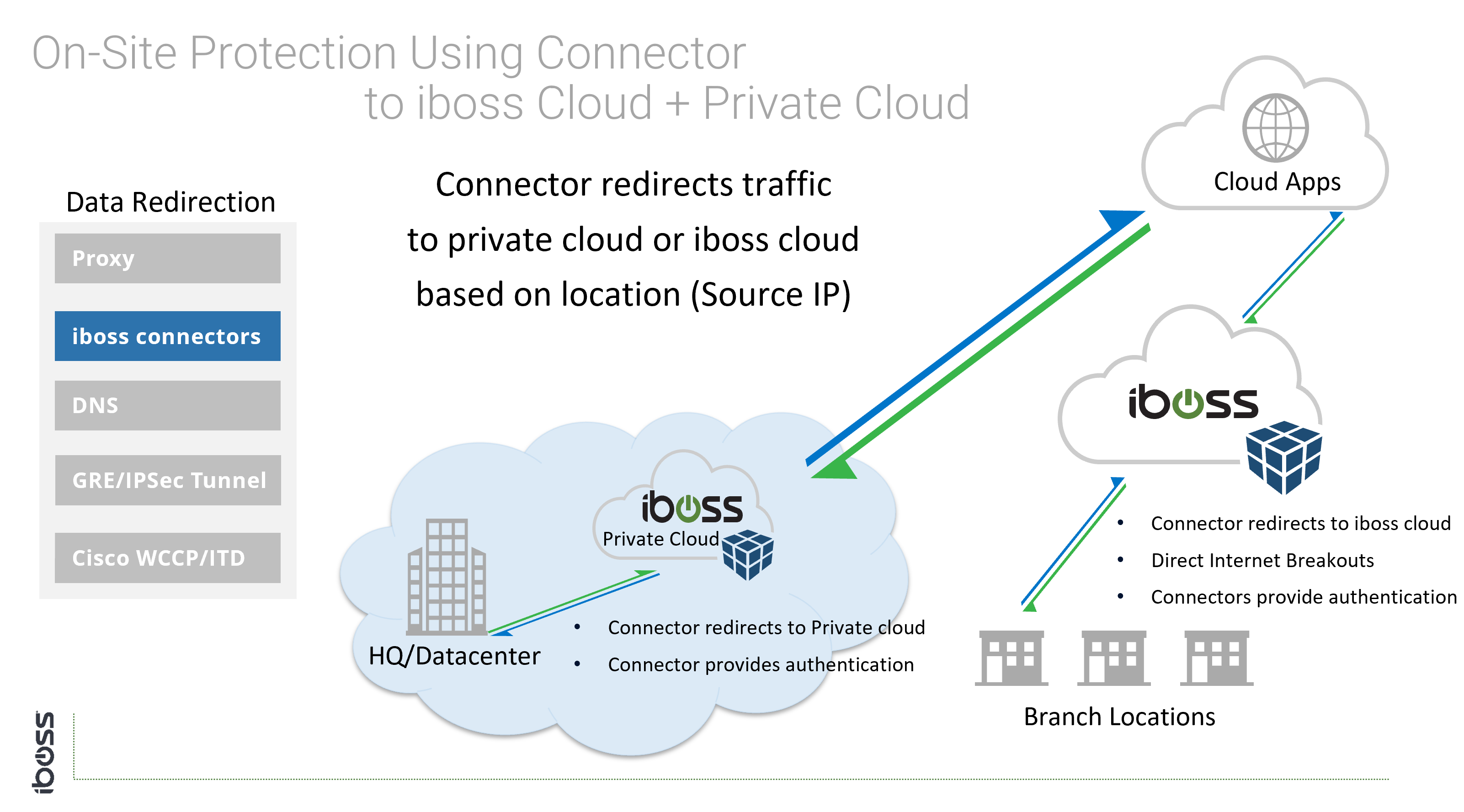
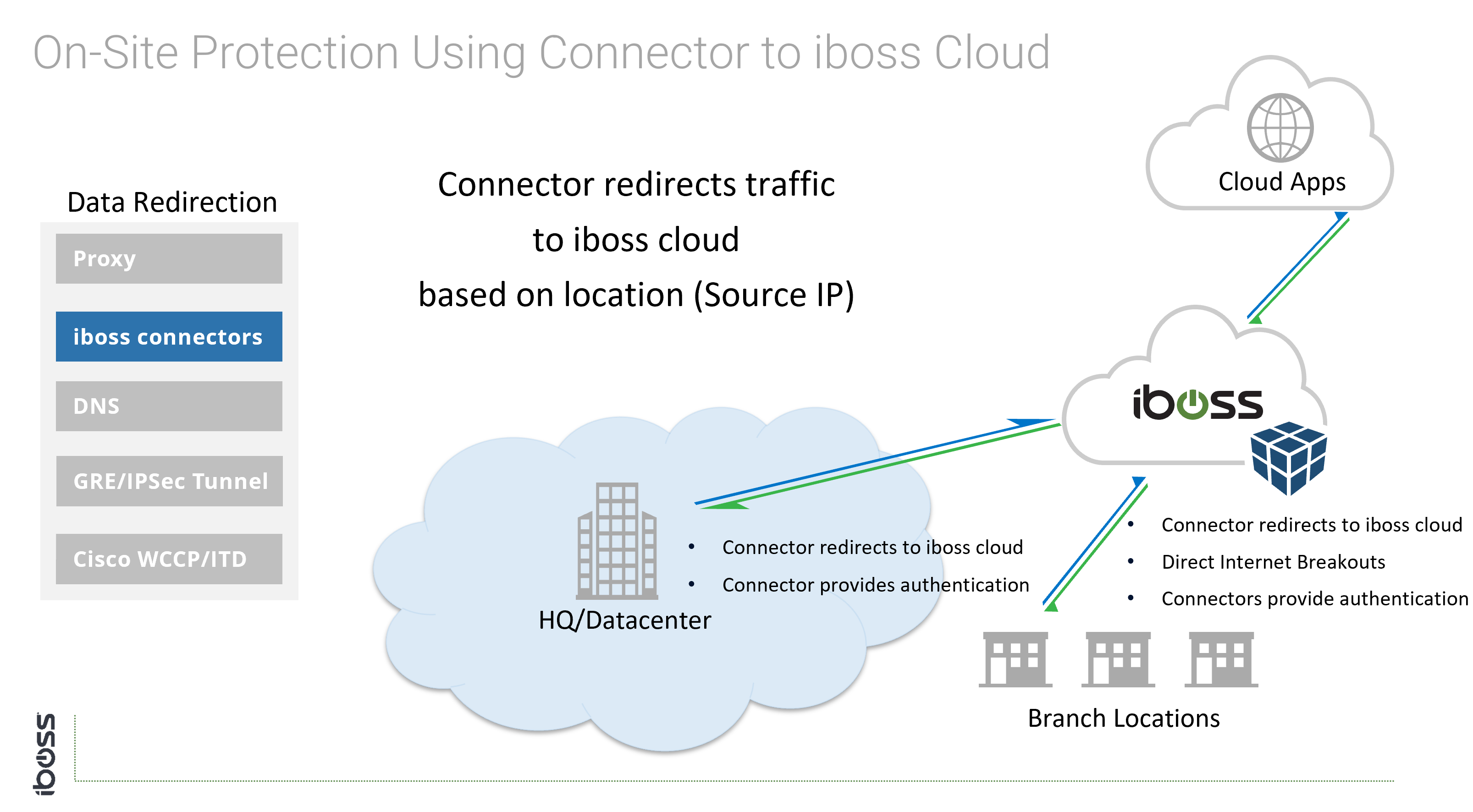
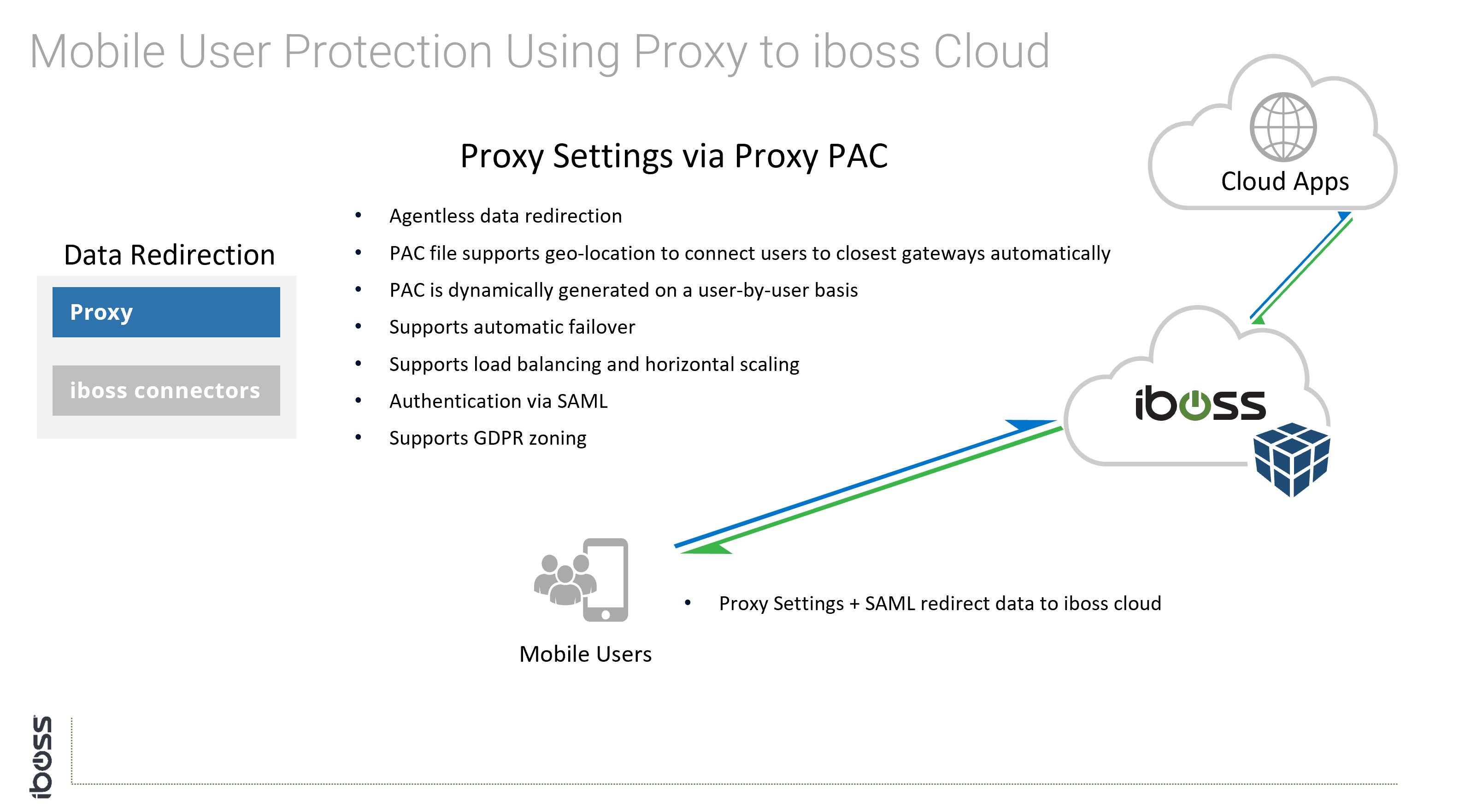
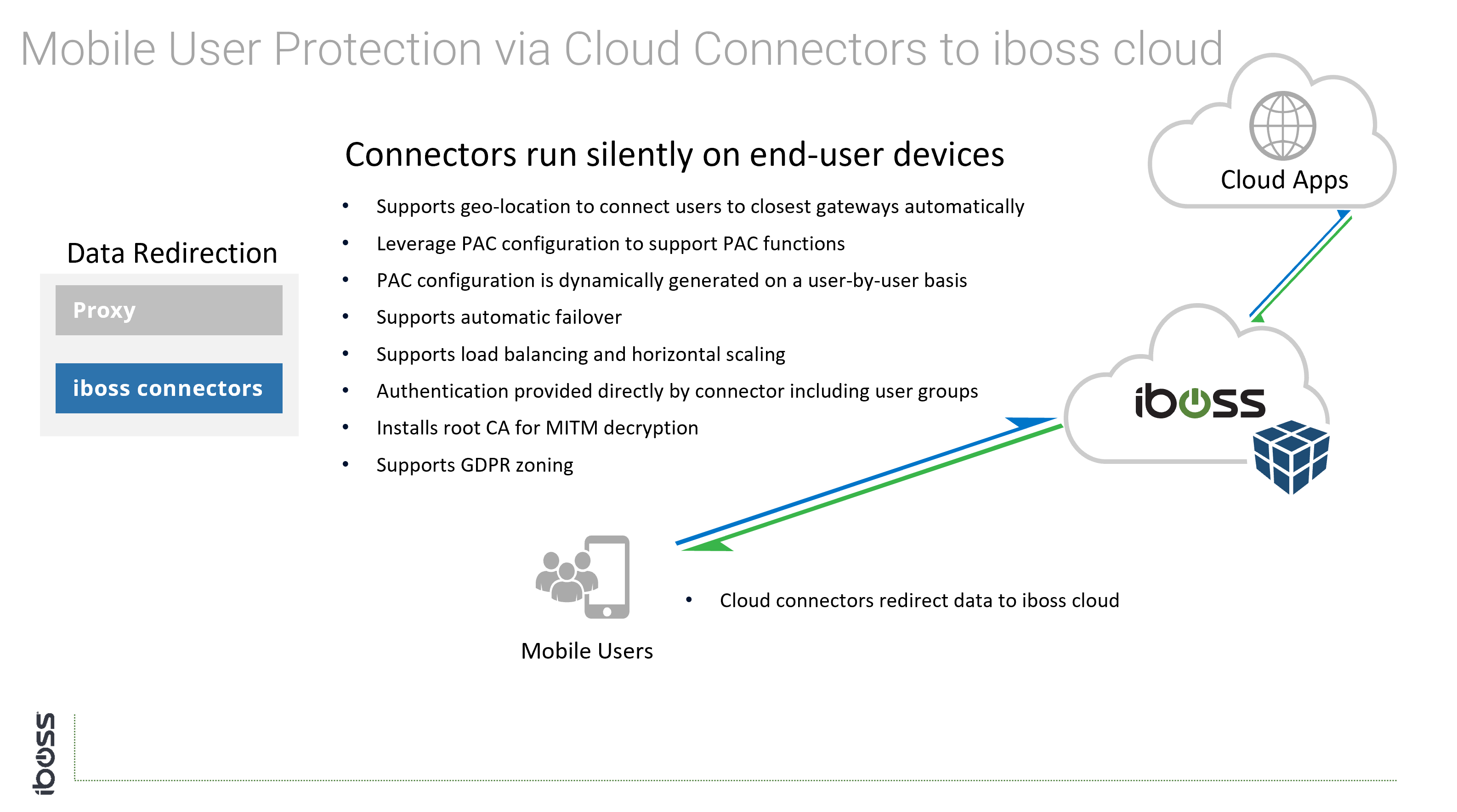
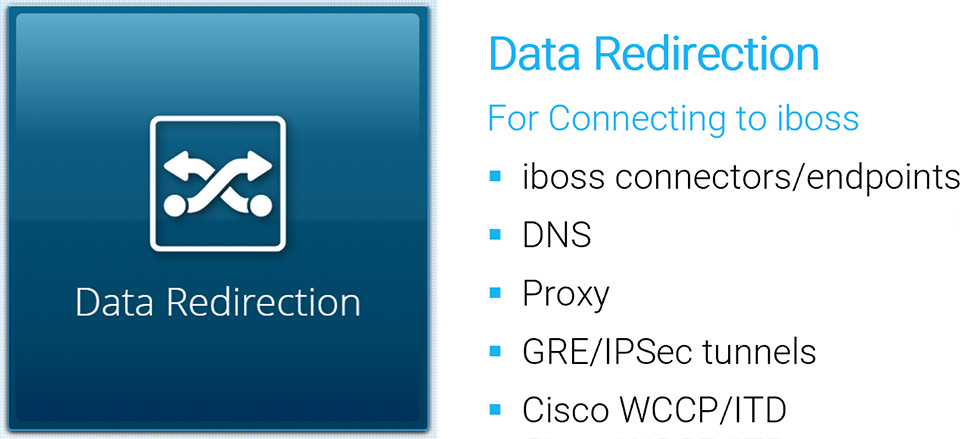
Generally speaking, creating tunnels from offices to the cloud service only applies to networks controlled by the organization (i.e. on-prem scenarios). The iboss cloud connectors (endpoints) and Proxy with SAML are connectivity methods that apply to users that are both on-network and off-network as tunnels are created directly between the user and the iboss cloud service. The iboss cloud connector are a popular choice because they simplify connecting users to the cloud service, provide user authentication, map group policy and install the root MITM certificate for SSL/TLS inspection.
Authentication is the process of identifying the end-user or device to apply a dynamic policy and associate logging and reporting to specific users. Authentication typically pairs with the connectivity method to provide both a connection to the cloud security service and the information required by IT teams to perform incident response.
Cloud Connectivity and User Authentication Methods
Cloud Connectivity Methods Ideal for On-Site and Mobile Users
Ideal methods for connecting users to iboss cloud include:
- Cloud connectors (iboss software that automatically and silently installs on endpoints)
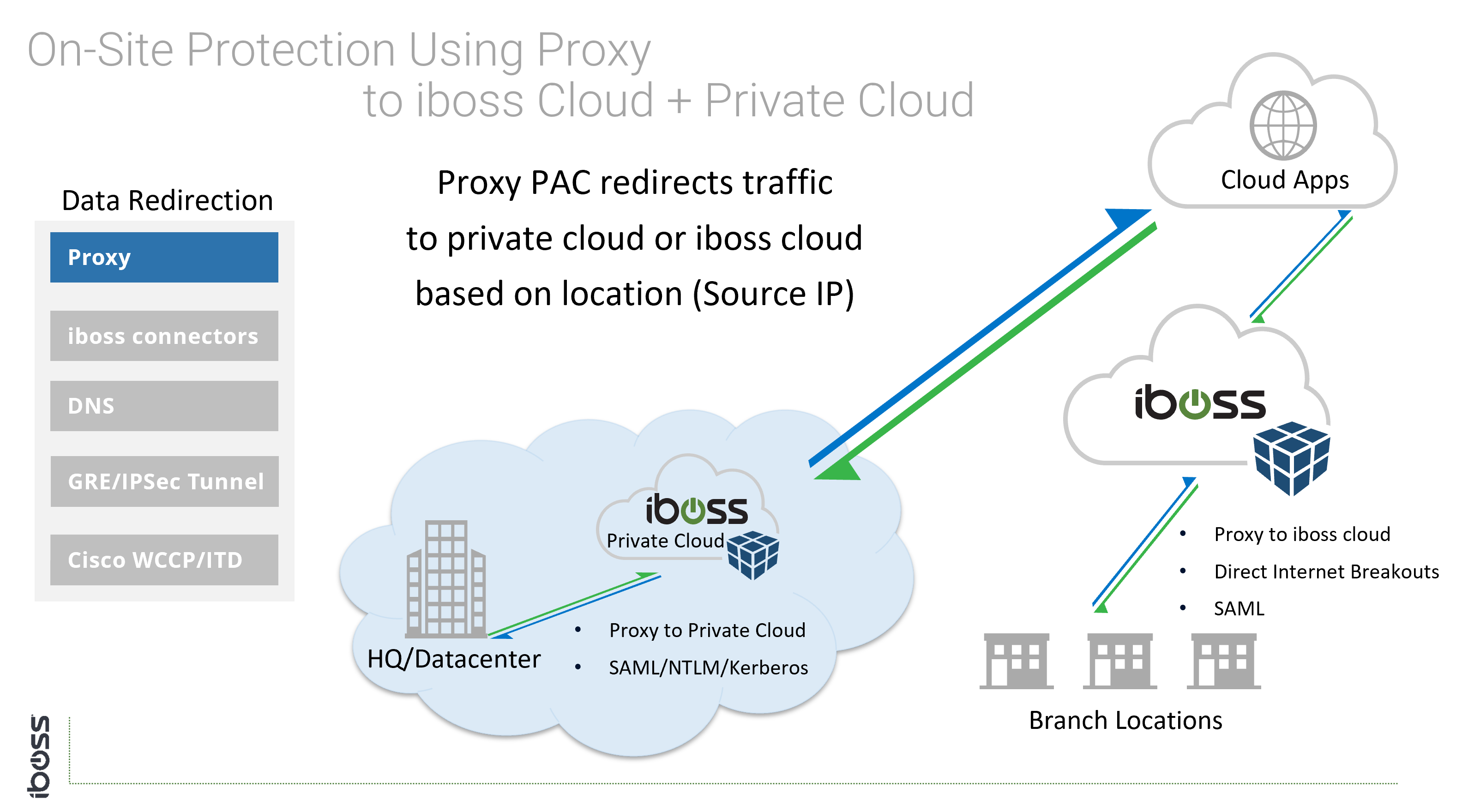
- Proxy – Settings configured and locked in the web browser
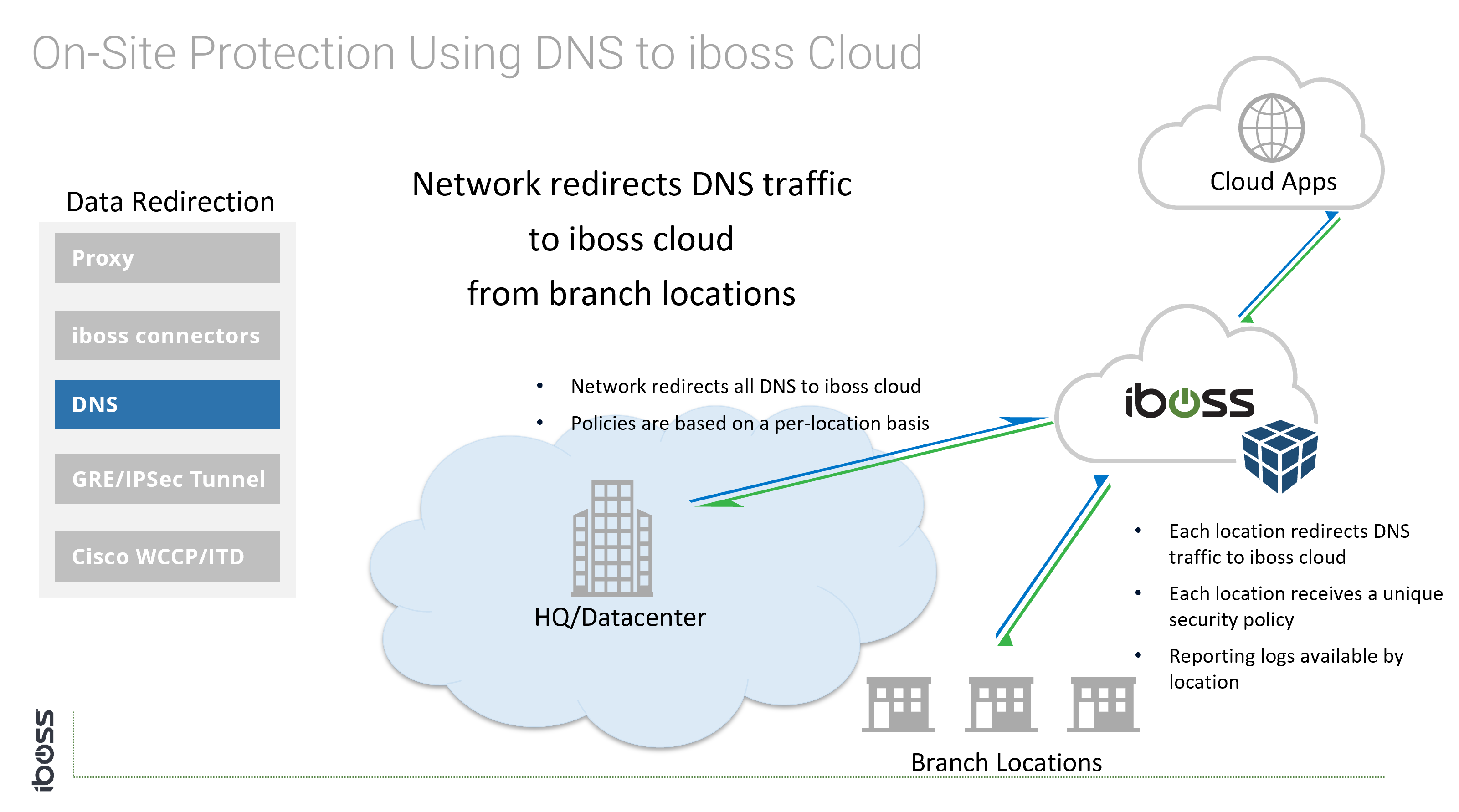
- DNS – DNS settings configured on the endpoint to point to iboss cloud
Cloud Connectors
- Thin iboss endpoints that redirect traffic to iboss. Support for GEO-Zoning dynamic traffic redirection, automatic load balancing and fail-over.
- Dynamically provide user identity and group membership and automatically install root CA for MITM decryption if necessary.
- Can transparently redirect all data on a device, across all ports.
- Available for all operating systems including Windows, Windows Terminal Servers, Apple iOS, macOS (OS X), Linux, and Android.
- Typically Pushed automatically and transparently via Group Policy or MDM.
Cloud Connectivity Methods for On-Site Users
The cloud connectivity methods that apply to mobile users can also apply to users on-site. With an eroding network perimeter, thinking in terms of connecting users to the cloud versus connecting physical offices is always a good choice. For example, it is possible a user that is on site joins a guest Wi-Fi network while sitting inside of the office. Connectivity methods that follow users are agnostic to the type of connection the device is utilizing. Users are always connected to the cloud security service at all times.
The following options are available for connecting physical perimeters to the iboss cloud security service:
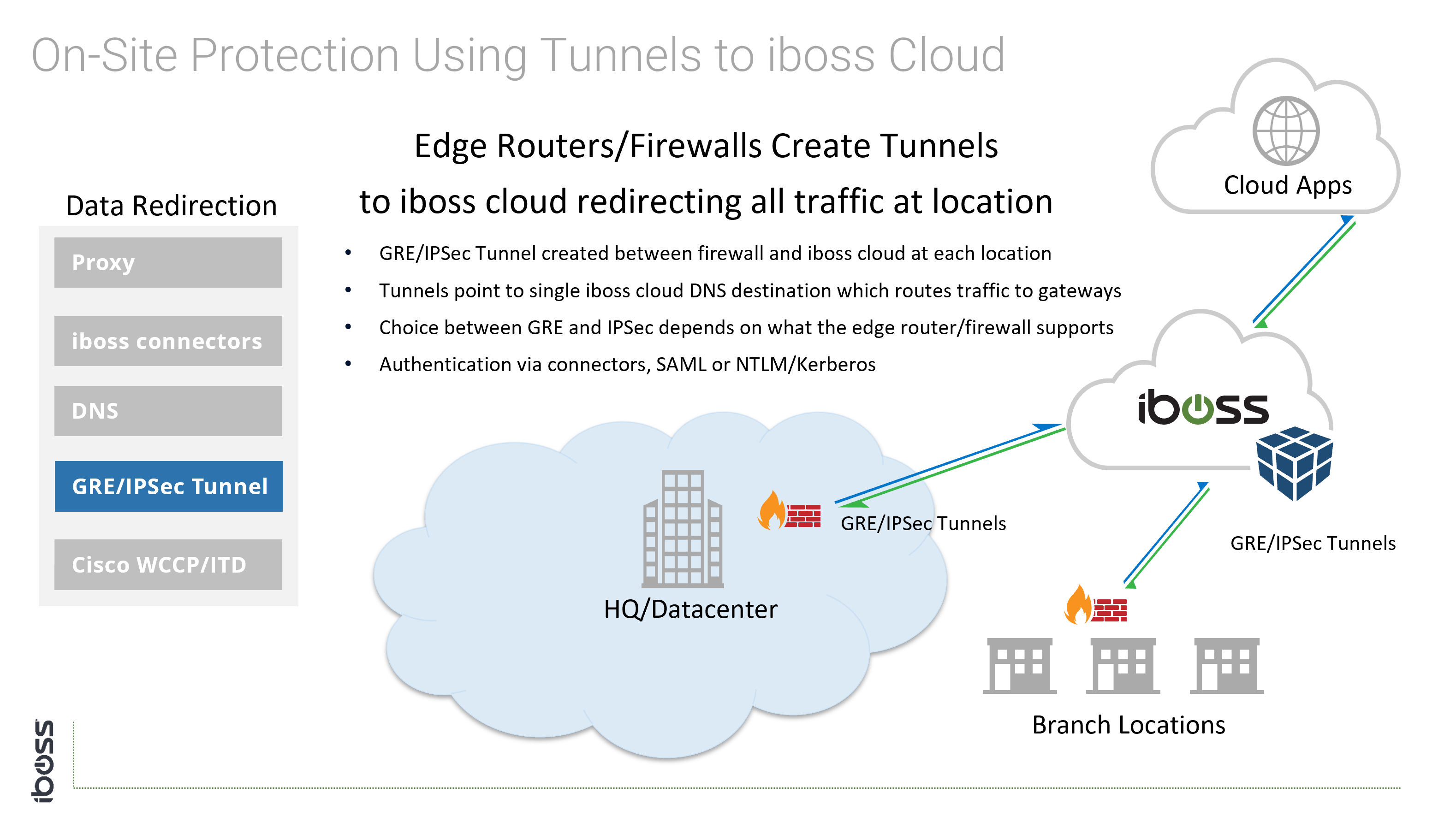
- GRE Tunnels – The tunnel is established between a router or firewall to the iboss cloud
- IPSec Tunnels – The tunnel is established between a router or firewall to the iboss cloud
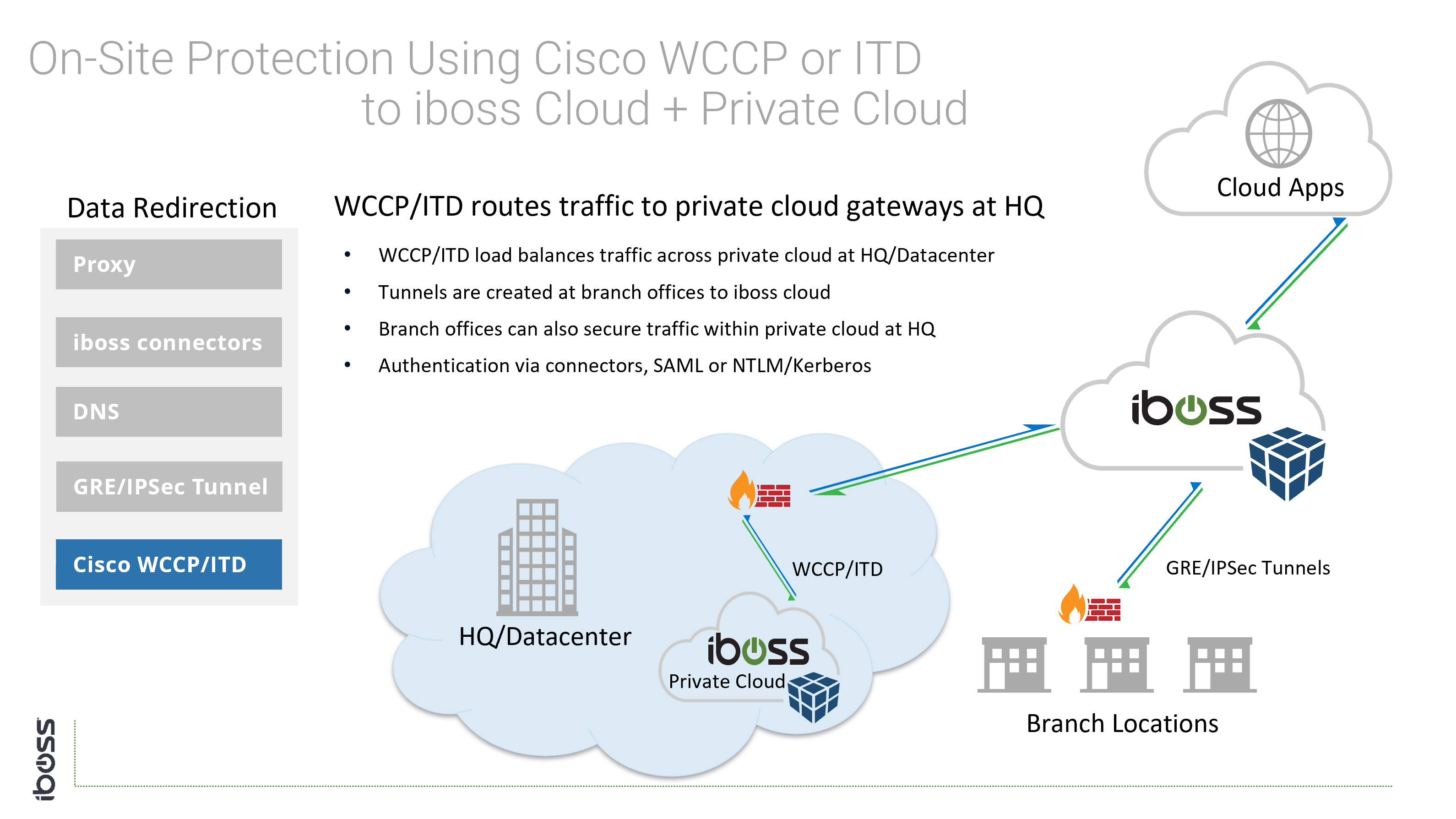
- WCCP/ITD – Typically used on Cisco Routers to redirect traffic to private cloud capacity
Since the network administrator has control of traffic flows and network equipment, the above options are available because they require configuration of networking equipment.
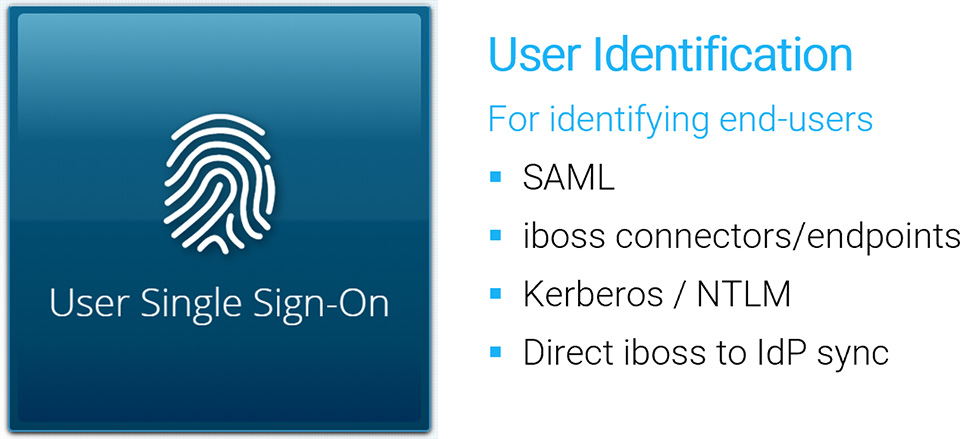
End-User Authentication




Connecting users to the iboss cloud ensures clean and secure connections to cloud applications and the Internet. In addition to connecting users to the iboss cloud, ensuring that the user identity is associated with the right policies and logging data is just as important. The iboss cloud provides a variety of methods for automatically and transparently obtaining end-user identity.
The iboss cloud connectors are a popular choice for obtaining identity and group membership information due to the ease of deployment and additional benefits they provide, such as automatically installing MITM decryption certificates. They can also be pushed out via Active Directory or Mobile Device Management (MDM).
There are many methods for authenticating end-users which are listed below.
Deployment Scenarios
The iboss cloud is built on a containerized architecture to deliver consistency of features and security regardless of deployment model, connectivity method or user location. Some of the core benefits of the iboss cloud include:
- Containerized architecture allows the iboss cloud to extend into the private cloud to form a private Point of Presence (PoP)
- All deployment methods covered will deliver the same capabilities and feature-set
- The platform is delivered as a complete SaaS offering, in the cloud, ensuring more time for policies and security versus managing infrastructure
- A single policy-set is managed regardless of deployment scenario
- A single pane of glass is used for administration
The following deployment scenarios are not exhaustive but show various options for connecting users and networks to iboss cloud.